Lensed fibers and traditional optical fibers differ significantly in terms of optical performance, application areas, and manufacturing processes. Lensed fibers utilize built-in lens structures to guide and focus light beams, offering unique advantages, while traditional optical fibers are primarily used for long-distance signal transmission. This article compares the two to help readers understand their characteristics and suitable applications.
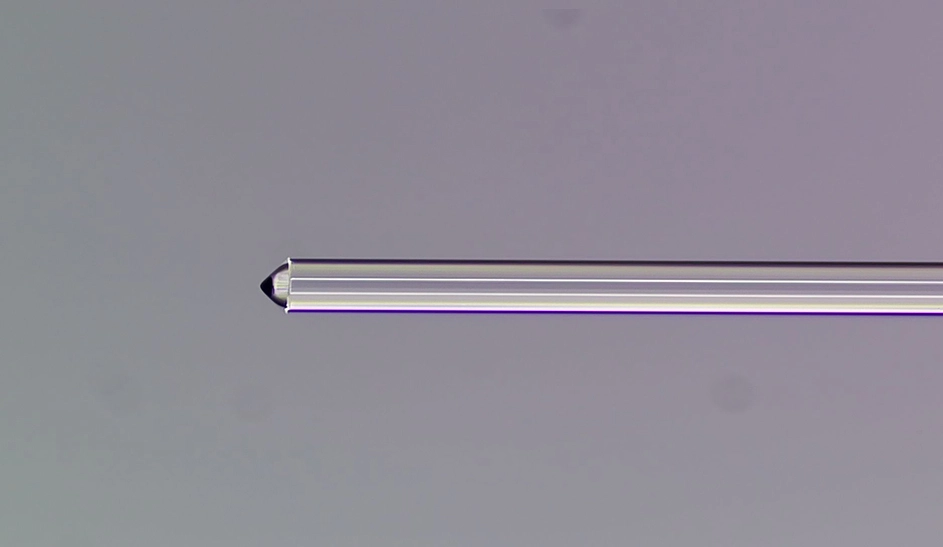
The most notable difference between lensed fiber array and traditional optical fibers lies in beam control and focusing. Traditional optical fibers transmit light signals based on the principle of total internal reflection, with light traveling through the fiber core without any focusing capability. In contrast, lensed fibers incorporate built-in lenses that can focus or expand light beams. Lensed fibers can precisely focus beams, making them widely used in laser systems, sensors, and precision optical instruments.
Lensed fibers like tapered lensed fiber and traditional optical fibers serve different purposes. Traditional optical fibers are mainly used in telecommunications, especially for long-distance transmission such as fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) and optical networks. Lensed fibers, due to their beam control capabilities, are more commonly applied in laser devices, medical imaging, industrial inspection, and optical sensing. In these applications, lensed fibers offer greater precision than traditional fibers.
The manufacturing process of lensed fibers is more complex than that of traditional optical fibers. Traditional optical fibers are produced using a fiber drawing process, which is relatively simple and low-cost. In contrast, lensed fibers require the integration of optical lenses on the fiber end-face or within the fiber, making the manufacturing more challenging and expensive. The precise design of lensed fibers involves advanced technologies such as microfabrication and laser etching to ensure the high accuracy of the lens structure.
There are also differences in optical loss and transmission efficiency. Traditional optical fibers are optimized for low loss, making them ideal for long-distance communication. Lensed fibers, due to the integrated lens, may introduce some optical loss. However, in specific applications, the advantages of beam control outweigh this drawback, and the overall performance remains high.
In conclusion, lensed fibers and traditional optical fibers differ in beam control, application fields, and manufacturing complexity. Lensed fibers offer superior performance in high-precision applications thanks to their ability to guide and focus light accurately, while traditional optical fibers are favored for efficient signal transmission in the communications industry. Choosing the appropriate fiber type based on specific requirements can yield the best results.
 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  2F, BLDG 6, #168, Changshan IZ, Liulian, Pingdi, Longgang District, Shenzhen, China
2F, BLDG 6, #168, Changshan IZ, Liulian, Pingdi, Longgang District, Shenzhen, China